CBSE is an abbreviation of Central Board in Education. It is the main body of school education in this nation. The board offers classes to students right from primary level through class 10 or 12. To protect the interest of students and parents, the board issues a syllabus every year.

In order to succeed in Syllabus for Class 11 Science in the Indian education system, one must be able to demonstrate competency and understanding of a variety of topics. Practicals are exams that measure one’s ability to apply concepts and recognize errors. To perform well on these exams, students have to know how the practical works are done. The practice exam PrepMinistry provides below will give you the rundown of what kinds of questions you might see. This is not intended to replace your studies or your efforts, just act as another tool if you choose to make use of it.
As an upcoming CBSE Class 11 student it’s vital not to overlook the practical portion of your annual assessment. The practicals carry a significant percentage of your overall marks and by not preparing properly you could be making yourself vulnerable to achieving a lower grade in the subject. We understand that because it is such an important aspect of your studies in this field it may be hard keeping track of all that is required for the different experiments or projects but have compiled the latest CBSE Syllabus for putting together practicals for nearly every concept that has been introduced throughout this term including those on Gases, Miscellaneous Chemistry, corrosion and much more.
CBSE Class 11 students must understand the importance of practicals and what they contribute towards the annual assessment. They are compulsory and have been allocated a set amount of marks. Practicals help students to improve their basics and enabling them to grasp concepts that they may otherwise fail to understand in dealing with theory only. Students should study the current CBSE Syllabus in order to be well informed about what specific experiments need to be done under each chapter. The list attached below contains the selected experiments (with their weightage), evaluation scheme, and projects assigned for the upcoming academic year, 2022-2023 for classes XI & XII Chemistry students.
CBSE Class 11 students in the Science stream must understand the value of practicals that help them in improving their basics and clear the concepts. Practicals carry a weighatge of 30 marks towards the annual assessment. Students should learn to perform all the experiments mentioned in the latest CBSE Syllabus. We have provided below the CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Practicals Syllabus that has been released for the current academic session, 2022-2023. Check below the list of experiments, evaluation scheme and projects suggested for the annual assessment. Students can check and download the CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus 2022-2023 in PDF.
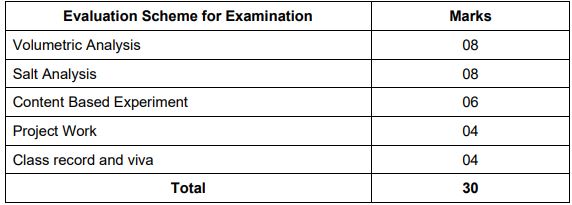
Check CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Practical Syllabus 2022-2023 below:
PRACTICALS (Total Periods: 60)
3 HOURS/ 30 Marks
PRACTICAL SYLLABUS (Total Periods: 60)
Micro-chemical methods are available for several of the practical experiments, wherever possible such techniques should be used.
A.Basic Laboratory Techniques
1. Cutting glass tube and glass rod
2. Bending a glass tube
3. Drawing out a glass jet
4. Boring a cork
B.Characterization and Purification of Chemical Substances
1. Determination of melting point of an organic compound.
2. Determination of boiling point of an organic compound.
3. Crystallization of impure sample of any one of the following: Alum, Copper Sulphate, Benzoic Acid.
C.Experiments based on pH 1.
Any one of the following experiments:
• Determination of pH of some solutions obtained from fruit juices, solution of known and varied concentrations of acids, bases and salts using pH paper or universal indicator. •
• Comparing the pH of solutions of strong and weak acids of same concentration. Study the pH change in the titration of a strong base using universal indicator. 2. Study the pH change by common-ion in case of weak acids and weak bases.
D.Chemical Equilibrium One of the following experiments:
1. Study the shift in equilibrium between ferric ions and thiocyanate ions by increasing/decreasing the concentration of either of the ions.
2. Study the shift in equilibrium between [Co(H2O)6]2+ and chloride ions by changing the concentration of either of the ions.
E.Quantitative Estimation
1. Using a mechanical balance/electronic balance.
2. Preparation of standard solution of Oxalic acid.
3. Determination of strength of a given solution of Sodium hydroxide by titrating it against standard solution of Oxalic acid.
4. Preparation of standard solution of Sodium carbonate.
5. Determination of strength of a given solution of hydrochloric acid by titrating it against standard Sodium Carbonate solution.
F.Qualitative Analysis
1.Determination of one anion and one cation in a given salt
Cation: Pb2+, Cu2+ As3+, Aℓ3+, Fe3+, Mn2+, Zn2+, Ni2+, Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+, Mg2+, NH4+
Anions: (CO3) 2- , S2- , (SO3) 2- , (NO2) - , (SO4) 2- , Cℓ- , Br- , I- , (PO4) 3- , (C2O4) 2- , CH3COO-, NO3 -
(Note: Insoluble salts excluded)
G.PROJECTS
Scientific investigations involving laboratory testing and collecting information from other sources. A few suggested Projects
• Checking the bacterial contamination in drinking water by testing sulphide ion • Study of the methods of purification of water
• Testing the hardness, presence of Iron, Fluoride, Chloride, etc., depending upon the regional variation in drinking water and study of causes of presence of these ions above permissible limit (if any).
• Investigation of the foaming capacity of different washing soaps and the effect of addition of Sodium carbonate on it • Study the acidity of different samples of tea leaves.
• Determination of the rate of evaporation of different liquids.
• Study the effect of acids and bases on the tensile strength of fibers.
• Study of acidity of fruit and vegetable juices.
Note: Any other investigatory project, which involves about 10 periods of work, can be chosen with the approval of the teacher.
PRACTICAL EXAMINATION FOR VISUALLY IMPAIRED STUDENTS
Note: Same Evaluation scheme and general guidelines for visually impaired students as given for Class XII may be followed.
A.List of apparatus for identification for assessment in practical (All experiments)
Beaker, tripod stand, wire gauze, glass rod, funnel, filter paper, Bunsen burner, test-tube, test-tube stand, dropper, test tube holder, ignition tube, china dish, tongs, standard flask, pipette, burette, conical flask, clamp stand, dropper, wash bottle
- Odour detection in qualitative analysis
- Procedure/Setup of the apparatus
B.List of Experiments A. Characterization and Purification of Chemical Substances
1.Crystallization of an impure sample of any one of the following: copper sulphate, benzoic acid
C.Experiments based on pH
1.Determination of pH of some solutions obtained from fruit juices, solutions of known and varied concentrations of acids, bases and salts using pH paper
2.Comparing the pH of solutions of strong and weak acids of same concentration.
D.Chemical Equilibrium
1.Study the shift in equilibrium between ferric ions and thiocyanate ions by increasing/decreasing the concentration of either ions.
2.Study the shift in equilibrium between [Co(H2O)6]2+ and chloride ions by changing the concentration of either of the ions.
E.Quantitative estimation
1.Preparation of standard solution of oxalic acid.
2.Determination of molarity of a given solution of sodium hydroxide by titrating it against standard solution of oxalic acid.
F.Qualitative Analysis
1.Determination of one anion and one cation in a given salt
2.Cations - NH4+
Anions - (CO3)2–, S2–, (SO3)2– , Cl– , CH3COO–
(Note: insoluble salts excluded)
3.Detection of Nitrogen in the given organic compound.
4.Detection of Halogen in the given organic compound.
Note: The above practical may be carried out in an experiential manner rather than recording observations.
PRESCRIBED BOOKS:
- Laboratory Manual of Chemistry, Class XI Published by NCERT
Download the above syllabus in PDF from the following link: