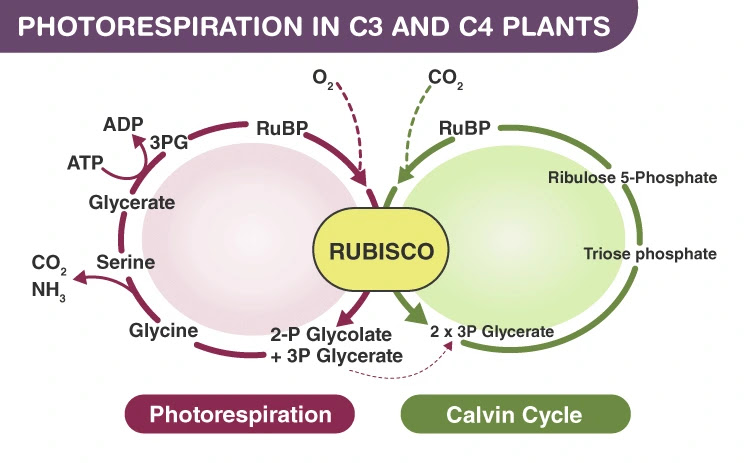
Plants, through the process of photosynthesis, make use of the sunlight to energise and generate glucose through the available water and carbon dioxide. This glucose through pathways can be converted into pyruvate. Through cellular respiration, pyruvate in turn gives ATP (adenosine triphosphate). ATP production can take place either aerobically (in the presence of oxygen) or anaerobically (absence of oxygen).
Structure of ATP Molecule
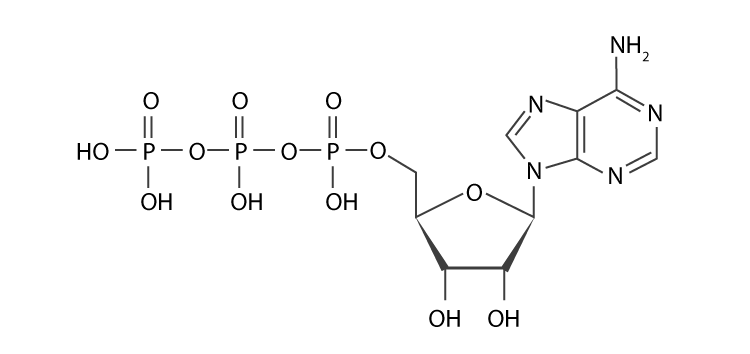
After every reaction, ATP molecules are recycled. These molecules are vital to providing energy to both exergonic and endergonic processes. The three phosphate groups found in this ATP molecule are high energy bonds as they are involved in releasing large amounts of energy when the bond breaks. This molecule renders energy for different life processes without which life cannot sustain itself.